Have you ever wondered how you solve complex problems, do math, see, taste, walk, read, and many more daily actions that we do everyday? 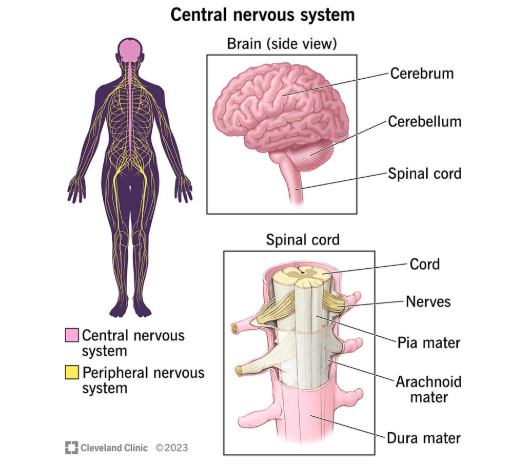
Your nervous system — especially your CNS (central nervous system which contains the brain and spinal cord) — are responsible for this. The nervous system is built from two major cell types: neurons, which do the sensing, info transferring, thinking, etc; and glial cells, which have four subtypes and help support and improve your neurons.
The anatomy of neurons
Neurons are made from 3 different parts. The cell body, or soma, contains the essential parts a cell needs to survive, like the mitochondria. The axon is a long extension from the cell body that sends signals to other neurons. Dendrites are small branch-like extensions that receive signals from other axons.
How do neurons communicate?
Neurons use 2 main ways to communicate, electricity and neurotransmitters. Neurotransmitters are chemicals that are exchanged between synapses, a small gap where dendrites and axons meet.
There are 2 types of neurotransmitters. Excitatory neurotransmitters encourage activity in neurons, and Inhibitory neurotransmitters slow activity in neurons.
Some essential neurotransmitters:
- Glutamate: most common excitatory neurotransmitter
- GABA(Gamma-aminobutyric acid): Most common inhibitory neurotransmitter
- Dopamine: Excitatory, responsible for reward, unstable level correlated to PD(Parkisons) or schizophrenia.
- Serotonin: Inhibitory, important for sleep, mood, and reproduction. Commonly deficient in mental illness like Bipolar, treated with SSRIs(selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor).
- Epinephrine and norepinephrine: Also known as adrenaline and noradrenaline, responsive for fight flight and stress response.
- Adenosine: Inhibitory, responsible for making you tired so you sleep. Caffeine works by blocking adenosine from entering its receptors, delaying sleep until the caffeine dissipates.
- ACh(Acetylcholine): Excitatory, responsible for muscles, REM sleep, memory, etc. Memory problems in Alzheimer’s are caused by acetylcholinesterase, which lowers ACh levels. Treatments for this include cholinesterase inhibitors.
Myelination:
Myelin is a fatty white covering around axons of a neuron. This makes neurons transmit signals 100x faster, as myelin insulates like how rubber insulates in wires. Myelinated neurons have small sections without myelin. These are called nodes of Ravier, and allow for saltatory conduction, where signals jump between each node of Ravier. Oligodendrocytes(a type of glial cell) make myelination in CNS, Schwann cells in the PNS(peripheral nervous system). 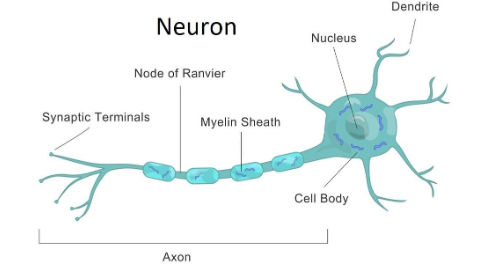
Sources: https://www.brainfacts.org/-/media/Brainfacts2/BrainFacts-Book/Brain-Facts-PDF-with-links.pdf
